While bitcoin (BTC) captures the attention of institutional narratives, Ethereum’s ether (ETH) stands out as the primary go-to token for traders seeking to maximize returns through leverage.
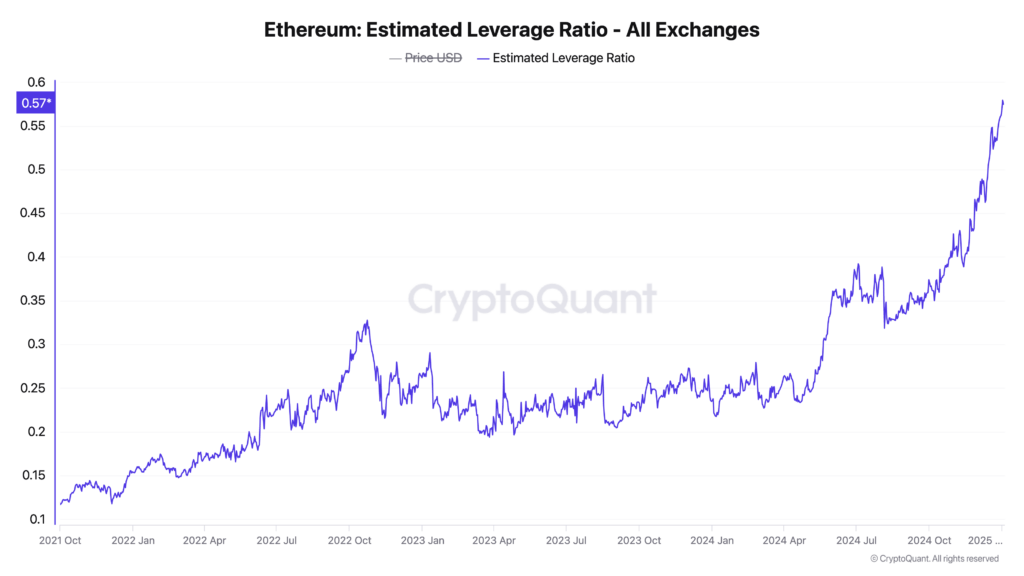
Ether’s estimated leverage ratio, which measures the degree of leverage employed by traders, rose to a new high of 0.57 on Wednesday, marking a significant increase from 0.37 at the start of the final quarter of 2024, data tracked by analytics firm CryptoQuant shows.
The ratio is calculated by dividing the accumulated open interest in standard futures and perpetual futures contracts listed worldwide by the total number of ETH in wallets linked to exchanges that offer futures trading.
A growing proportion suggests that traders are increasingly using leverage, indicating an increase in risk-taking and speculation in the market. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions in the market with a relatively small pool of capital.
For example, if an exchange offers a leverage ratio of 10:1, a trading entity can control a position worth $10,000 with just $1,000 in margin deposit. The use of leverage magnifies both profits and losses and increases the risk of liquidations (forced closures due to tight margins) when the market moves against leveraged positions, a dynamic that often generates volatility.
Ether’s leverage ratio of over 0.5 means that a significant amount of leverage trading is occurring in the futures market relative to the availability of real coins in exchange wallets.
Ether’s leverage ratio of over 0.5 indicates that a substantial amount of leveraged trading is taking place in the futures market compared to the actual coins available in exchange wallets.
This level of leverage is considerably higher than Bitcoin, which has an estimated leverage ratio of 0.269 at the time of this publication, the highest since early 2023, but still well below the all-time high of 0.36 seen. in October 2022.
So, don’t be surprised if ether experiences twice the price volatility of bitcoin in the near future.