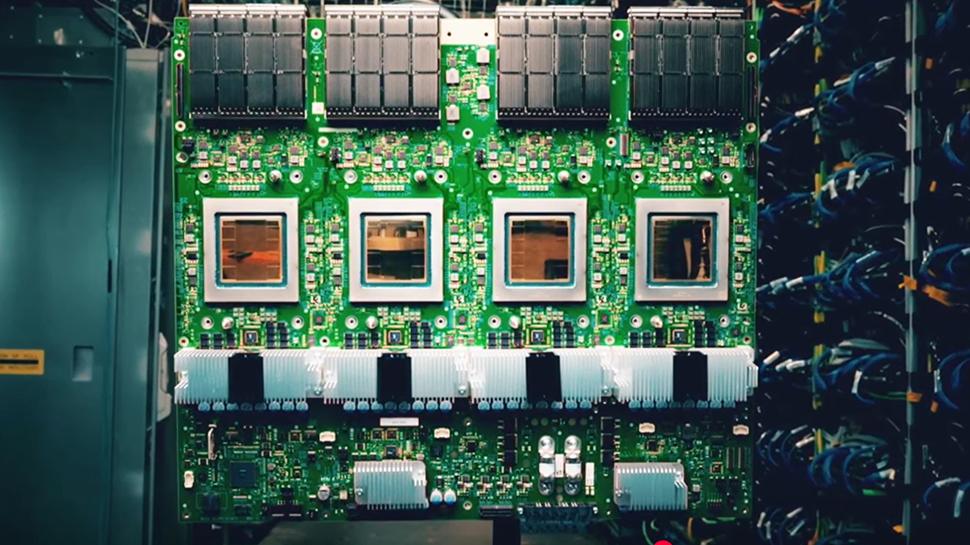
- The Google Ironwood TPU scale at 9216 chips with 1.77pb shared memory
- The dual architecture DUE DELIVER 4614 TFLOPS FP8 and 192GB HBM3E by chip
- The improved reliability refrigeration characteristics and design assisted by AI allow efficient inference workloads on scale
Google closed automatic learning sessions at the recent Hot Chips 2025 event with a detailed look at its new tensioner processing unit, Ironwood.
The chip, which was first revealed in Google Cloud Next 25 in April 2025, is the company’s first TPU designed mainly for large -scale inference work loads, instead of training, and arrives as its seventh generation of TPU hardware.
Each iron wood chip integrates two computing ratings, delivering 4,614 FP8 performance tflops, and eight HBM3E batteries provide 192 GB of memory capacity per chip, combined with 7.3TB/s bandwidth.
1.77pb of HBM
Google has incorporated 1.2 Tbps I/O bandwidth to allow a system to expand up to 9,216 chips per pod without glue logic. This configuration reaches a whopping 42.5 Performance exachers.
The memory capacity also scale in an impressive way. Through a capsule, Ironwood offers 1.77pb from HBM directly direct. This level establishes a new record for shared memory supercomputers, and is enabled by optical circuit switches that join.
The hardware can reconfigure around the failed nodes, restoring workloads from the control points.
The chip integrates multiple characteristics aimed at stability and resilience. These include a confidence root in chip, incorporated self -expression functions and measures to mitigate the corruption of silent data.
Logical repair functions are included to improve manufacturing performance. An emphasis is seen in RA, or reliability, availability and service capacity, throughout architecture.
The cooling is handled by a cold plate solution backed by the third generation of Google liquid cooling infrastructure.
Google claims a double improvement in watt yield compared to Trillium. Dynamic voltage and frequency scale even more improvement efficiency during varied workloads.
Ironwood also incorporates AI techniques within its own design. It was used to help optimize circuits and the ALU plane.
A fourth generation record has been added to accelerate integrities and collective operations, which supports workloads such as recommendation engines.
The implementation is already underway in Hyperscale on Google Cloud Data Centers, although the TPU remains an internal platform that is not directly available to customers.
Comment at the Hot Chips 2025 session, ServethehomeRyan Smith said: “This was an incredible presentation. Google saw the need to create a calculation of high -end AI does many generations. Now the company is innovating at all levels from the chips, to the interconnections and physical infrastructure. Even when the last presentation of Hot Chips 2025 chips had the audience attached to the stage of what Google was showing.”