The study, conducted by Gavi, the Vaccina Alliance, in collaboration with the Burnet Institute of Australia, and published in the Global Health British Medical Journal, He analyzed 210 outbreaks in 49 low -income countries for a period of 23 years.
He found that the rapid deployment of the vaccine during the sprouts of anger, ebola, measles, meningitis and yellow fever, had led to estimated reductions in diseases and deaths of almost 60 percent on average.
For diseases such as yellow fever and ebola, the impact was even more dramatic: yellow fever deaths decreased by 99 percent, while Ebola deaths fell by 76 percent.
The results highlight not only the effectiveness of emergency vaccination, but also the critical role of preparation and speed in response to emerging threats.
“For the first time, we can thoroughly quantify the benefit, in human and economic terms, to display vaccines against outbreaks of some of the most mortal infectious diseases,” said Sania Nishtar, CEO of Gavi.
“This study clearly demonstrates the power of vaccines as a profitable countermelted for the growing risk facing the world of shoots.“
Gavi: an association that saves lives
Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, is a unique global association that helps vaccinate almost half of the world’s children against mortal and weakening diseases.
It brings together the governments of developing countries and donors, the World Health Organization (WHO), the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF), the World Bank, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and other key partners to expand access to immunization.
Gavi also maintains global vaccines reserves for important diseases, managed in coordination with WHO, UNICEF, Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) and the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Rescue Societies (IFFRC).
Working in association with Gavi, governments and health authorities, UN agencies support vaccination campaigns in some of the most remote regions of writing. In the photo, a child receives a vaccine on the Solomon Islands in the Pacific.
Quantify lives and costs saved
In addition to reducing deaths and years of life adjusted for disability, emergency vaccination during the 210 outbreaks studied generated almost $ 32 billion in economic benefits, since the avoidance of premature deaths and years of life lost due to disability.
The authors of the study say that this figure is probably a conservative estimate, since it does not include the broader social and macroeconomic impacts of the important outbreaks.
For example, the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, which occurred before there was an approved vaccine, cost the region an estimated $ 53 billion. In contrast, the posterior shoots responded with emergency vaccines saw reduced deaths in three quarters and the threat of regional propagation was drastically reduced.
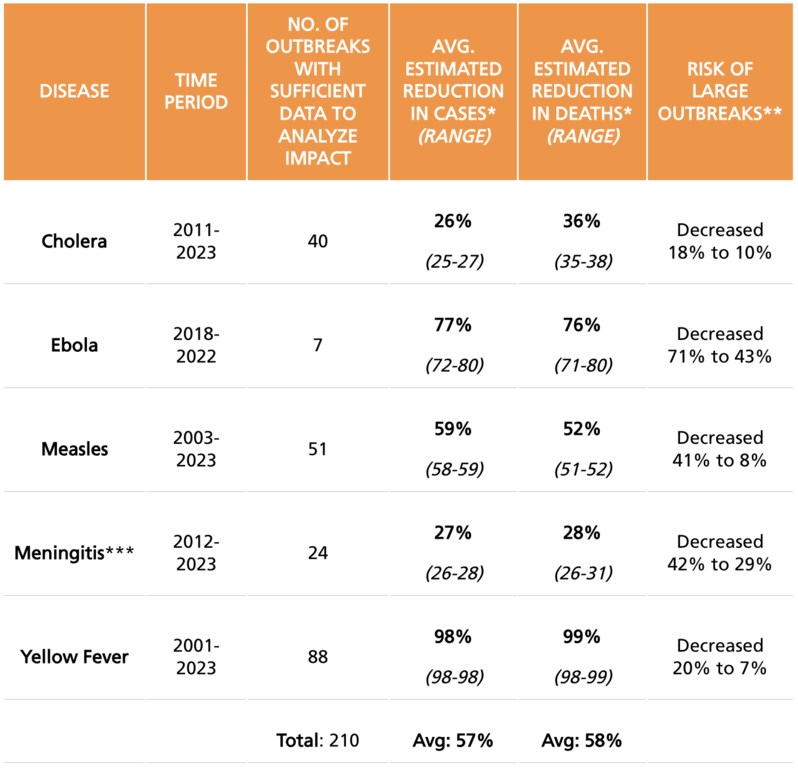
Disease results
Illness disease.
The study provides a breakdown of the effectiveness of the disease.
MeaslesOne of the most known infectious viruses, cases fell 59 percent and deaths by 52 percent thanks to outbreak response campaigns.
Yellow fever He saw the greatest profits, with emergency vaccination almost eliminating deaths, a 99 percent drop.
Anger and meningitisthat often attack communities with limited medical care access and infrastructure, saw more modest but still significant reductions in cases and deaths.
Vaccines helped reduce cholera cases and deaths by 28 percent and 36 percent, respectively, in 40 outbreaks of cholera between 2011 and 2023. For meningitis, cases and deaths fell by 27 % and 28 percent respectively, for 10 years.
Vaccines, Covid-19 and future threats
The Coronavirus “> Covid-19 pandemic was a marked reminder of the value of vaccines, which saved approximately 20 million lives worldwide in the first year of deployment aloneaccording to the respected and influential journal medical lancet.
However, pandemic also interrupted routine immunization, which led to a dangerous refund in coverage rates for diseases such as measles and polyomyelitis. The Gavi study emphasizes that emergency vaccination should be paired with strong routine immunization systems to avoid future outbreaks.
Looking towards the future, Gavi 2026-2030 strategy includes expanding reserves, accelerating access to vaccines for diseases such as MPOX and hepatitis E, and support preventive campaigns in high-risk regions.